Spark Catalyst Optimizer and spark Expression basics
Table of contents
- Overview
- Trees
- Rules
- Expression
- CodegenFallback
- Example of spark native function using Unary expression
Spark Catalyst Overview
- Core of Spark dataframe API and SQL queries.
- Supports cost based and rule based optimization.
- Built to be extensible :
- Adding new optimization techniques and features
- Extending the optimizier for custom use cases
- At core it uses trees
- On top of it various libraries are written for query processing, optimization and execution.
Trees
- Trees in Catalyst consists of node objects.
- Node - type and zero/more children
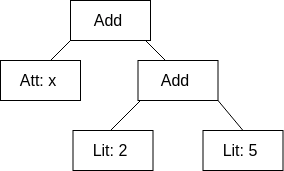
- E.g If Literal(v: Int), Attribute(name: String), Add(l: TreeNode, r: TreeNode) are simple node types then x+(2+5) can be represented as Add(Attribute(x), Add(Literal(2), Literal(5))).
Rules
- Function from a tree to another tree i.e modifying the tree.
- Replacing a pattern matched subtree with transformation. e.g Add(Literal(2), Literal(5)) => Literal(7)
- Transform method provided with catalyst tree e.g Recursively updates substructures to combine Literals
tree.transform {
case Add(Literal(c1), Literal(c2)) => Literal(c1+c2)
}
So, x + (2+5) => x + 7
Expression
- Executable node in catalyst tree. Take inputs and evaluates them.
- Can generate java source from which can be used for evaluation (docodegen()).
- Should be deterministic. Like pure functions.
scala> import org.apache.spark.sql.catalyst.expressions.Expression
scala> import org.apache.spark.sql.catalyst.expressions.{Literal, Add}
// Expression and eval
scala> val e : Add(Literal(3), Literal(4))
scala> e.eval()
res0: Any = 7
// Deterministic?
scala> e.deterministic
res1: Boolean = true
| Type of Expression | Kind | Use |
|---|---|---|
| BinaryExpression | Abstract class | 2 children |
| CodegenFallback | trait | Interpreted mode, no code generation |
| UnaryExpression | Abstract Class | 1 child |
| LeafExpression | abstract class | No children |
| Unevaluable | trait | Cannot be evaluated to produce a value (neither in interpreted nor code-generated expression evaluations), e.g AggregateExpression |
- Expression contract :
package org.apache.spark.sql.catalyst.expressions
// only required methods that have no implementation
def dataType: DataType // Data type of the result of evaluating an expression
* The default behavior is to call the eval method of the expression. Concrete expression
* implementations should override this to do actual code generation.
def doGenCode(ctx: CodegenContext, ev: ExprCode): ExprCode
* Interpreted (non-code-generated) expression evaluation
* Slower than generated code('relative?')
def eval(input: InternalRow = EmptyRow): Any
def nullable: Boolean
}
CodegenFallback
- Trait derived from Expression which allows expressions to not support java code generation and go full interpreted mode.
- e.g
trait NoCodegenExp extends UnaryExpression with CodegenFallback {}
Example of spark native function using Unary expression
- Here we will write a native function using Codegen and CodegenFallback.
- Codegen example :
import org.apache.spark.sql.catalyst.expressions.{Expression, ImplicitCastInputTypes, UnaryExpression}
import org.apache.spark.sql.catalyst.util.DateTimeUtils
import org.apache.spark.sql.types.{DataType, DateType}
import org.apache.spark.unsafe.types.UTF8String
import org.apache.spark.sql.catalyst.expressions.codegen.{CodegenContext, ExprCode}
// Returns beginning of month date for a date
case class BeginningOfMonth(startDate: Expression)
extends UnaryExpression
with ImplicitCastInputTypes {
override def child: Expression = startDate
override def inputTypes: Seq[DataType] = Seq(DateType)
override def dataType: DataType = DateType
// .eval calls nullSafeEval if input is non-null else it returns null
override def nullSafeEval(date: Any): Any = {
val level = DateTimeUtils.parseTruncLevel(UTF8String.fromString("MONTH"))
DateTimeUtils.truncDate(date.asInstanceOf[Int], level)
}
override protected def doGenCode(ctx: CodegenContext, ev: ExprCode): ExprCode = {
val level = DateTimeUtils.parseTruncLevel(UTF8String.fromString("MONTH"))
val dtu = DateTimeUtils.getClass.getName.stripSuffix("$")
defineCodeGen(ctx, ev, sd => s"$dtu.parseTruncLevel($sd, $level)")
}
override def prettyName: String = "beginning_of_month"
}
- CodegenFallback example :
import org.apache.spark.sql.catalyst.expressions.{Expression, ImplicitCastInputTypes, UnaryExpression}
import org.apache.spark.sql.catalyst.expressions.codegen.CodegenFallback
import org.apache.spark.sql.catalyst.util.DateTimeUtils
import org.apache.spark.sql.types.{DataType, DateType}
import org.apache.spark.unsafe.types.UTF8String
import org.apache.spark.sql.catalyst.expressions.codegen.{CodegenContext, ExprCode}
// Returns beginning of month date for a date
case class BeginningOfMonth(startDate: Expression)
extends UnaryExpression
with ImplicitCastInputTypes with CodegenFallback{
override def child: Expression = startDate
override def inputTypes: Seq[DataType] = Seq(DateType)
override def dataType: DataType = DateType
// .eval calls nullSafeEval if input is non-null else it returns null
override def nullSafeEval(date: Any): Any = {
val level = DateTimeUtils.parseTruncLevel(UTF8String.fromString("MONTH"))
DateTimeUtils.truncDate(date.asInstanceOf[Int], level)
}
// override protected def doGenCode(ctx: CodegenContext, ev: ExprCode): ExprCode = {
// val level = DateTimeUtils.parseTruncLevel(UTF8String.fromString("MONTH"))
// val dtu = DateTimeUtils.getClass.getName.stripSuffix("$")
// defineCodeGen(ctx, ev, sd => s"$dtu.parseTruncLevel($sd, $level)")
// }
override def prettyName: String = "beginning_of_month"
}
- The can be registered and used in spark as :
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
....
// Register the function
object BegRegister extends NativeFunctionRegistration {
val expressions: Map[String, (ExpressionInfo, FunctionBuilder)] = Map(
expression[BeginningOfMonth]("beg_m")
)
}
BegRegister.registerFunctions(spark)
import spark.implicits._
val df = Seq(
(Date.valueOf("2020-01-15")),
(Date.valueOf("2020-01-20")),
(null)
).toDF("some_date")
df.show()
df.createTempView("dates")
val dfVal = spark.sql("SELECT beg_m(some_date) from dates")
dfVal.show()
}
- In codegenfallback example CodegenFallback trait is used and doGenCode() method is not required as eval(or nullSafeEval).
References :